Leukemia
Definition of Leukemia
Leukemia (American English) or leukaemia (British English) is a type of cancer of the blood or bone marrow characterized by an abnormal increase of immature white blood cells called “blasts”. Leukemia is a broad term covering a spectrum of diseases. In turn, it is part of the even broader group of diseases affecting the blood, bone marrow, and lymphoid system, which are all known as hematological neoplasms.
Leukemia is a treatable disease. Most treatments involve chemotherapy, medical radiation therapy, hormone treatments, or bone marrow transplant. The rate of cure depends on the type of leukemia as well as the age of the patient. Children are more likely to be permanently cured than adults. Even when a complete cure is unlikely, most people with a chronic leukemia and many people with an acute leukemia can be successfully treated for years. Sometimes, leukemia is the effect of another cancer, known as blastic leukemia, which usually involves the same treatment, although usually unsuccessful.
Classification:
Clinically and pathologically, leukemia is subdivided into a variety of large groups. The first division is between its acute and chronic forms:
Acute leukemia is characterized by a rapid increase in the number of immature blood cells. Crowding due to such cells makes the bone marrow unable to produce healthy blood cells. Immediate treatment is required in acute leukemia due to the rapid progression and accumulation of the malignant cells, which then spill over into the bloodstream and spread to other organs of the body. Acute forms of leukemia are the most common forms of leukemia in children.
Chronic leukemia is characterized by the excessive build up of relatively mature, but still abnormal, white blood cells. Typically taking months or years to progress, the cells are produced at a much higher rate than normal, resulting in many abnormal white blood cells. Whereas acute leukemia must be treated immediately, chronic forms are sometimes monitored for some time before treatment to ensure maximum effectiveness of therapy. Chronic leukemia mostly occurs in older people, but can theoretically occur in any age group.
Causes of Leukemia
There is no single known cause for any of the different types of leukemia. The few known causes, which are not generally factors within the control of the average person, account for relatively few cases. The cause for most cases of leukemia is unknown. The different leukemias likely have different causes.
Leukemia, like other cancers, results from mutations in the DNA. Certain mutations can trigger leukemia by activating oncogenes or deactivating tumor suppressor genes, and thereby disrupting the regulation of cell death, differentiation or division. These mutations may occur spontaneously or as a result of exposure to radiation or carcinogenic substances.
Among adults, the known causes are natural and artificial ionizing radiation, a few viruses such as human T-lymphotropic virus, and some chemicals, notably benzene and alkylating chemotherapy agents for previous malignancies. Use of tobacco is associated with a small increase in the risk of developing acute myeloid leukemia in adults. Cohort and case-control studies have linked exposure to some petrochemicals and hair dyes to the development of some forms of leukemia. Diet has very limited or no effect, although eating more vegetables may confer a small protective benefit.
Viruses have also been linked to some forms of leukemia. Experiments on mice and other mammals have demonstrated the relevance of retroviruses in leukemia, and human retroviruses have also been identified. The first human retrovirus identified was human T-lymphotropic virus, or HTLV-1, which is known to cause adult T-cell leukemia.
Some people have a genetic predisposition towards developing leukemia. This predisposition is demonstrated by family histories and twin studies. The affected people may have a single gene or multiple genes in common. In some cases, families tend to develop the same kinds of leukemia as other members; in other families, affected people may develop different forms of leukemia or related blood cancers.
In addition to these genetic issues, people with chromosomal abnormalities or certain other genetic conditions have a greater risk of leukemia. For example, people with Down syndrome have a significantly increased risk of developing forms of acute leukemia (especially acute myeloid leukemia), and Fanconi anemia is a risk factor for developing acute myeloid leukemia.
Signs and Symptoms of Leukemia
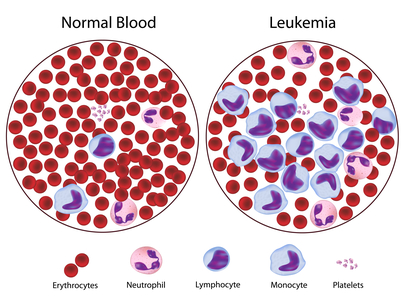 Damage to the bone marrow, by way of displacing the normal bone marrow cells with higher numbers of immature white blood cells, results in a lack of blood platelets, which are important in the blood clotting process. This means people with leukemia may easily become bruised, bleed excessively, or develop pinprick bleeds (petechiae).
Damage to the bone marrow, by way of displacing the normal bone marrow cells with higher numbers of immature white blood cells, results in a lack of blood platelets, which are important in the blood clotting process. This means people with leukemia may easily become bruised, bleed excessively, or develop pinprick bleeds (petechiae).
White blood cells, which are involved in fighting pathogens, may be suppressed or dysfunctional. This could cause the patient’s immune system to be unable to fight off a simple infection or to start attacking other body cells. Because leukemia prevents the immune system from working normally, some patients experience frequent infection, ranging from infected tonsils, sores in the mouth, or diarrhea to life-threatening pneumonia or opportunistic infections.
Finally, the red blood cell deficiency leads to anemia, which may cause dyspnea and pallor.
Some patients experience other symptoms, such as feeling sick, having fevers, chills, night sweats, feeling fatigued and other flu-like symptoms. Some patients experience nausea or a feeling of fullness due to an enlarged liver and spleen; this can result in unintentional weight loss. Blasts affected by the disease may come together and become swollen in the liver or in the lymph nodes causing pain and leading to nausea.
If the leukemic cells invade the central nervous system, then neurological symptoms (notably headaches) can occur. Uncommon neurological symptoms like migraines, seizures, or coma can occur as a result of brain stem pressure. All symptoms associated with leukemia can be attributed to other diseases. Consequently, leukemia is always diagnosed through medical tests.
The word leukemia, which means ‘white blood’, is derived from the disease’s namesake high white blood cell counts that most leukemia patients have before treatment. The high number of white blood cells are apparent when a blood sample is viewed under a microscope. Frequently, these extra white blood cells are immature or dysfunctional. The excessive number of cells can also interfere with the level of other cells, causing a harmful imbalance in the blood count.
Some leukemia patients do not have high white blood cell counts visible during a regular blood count. This less-common condition is called aleukemia. The bone marrow still contains cancerous white blood cells which disrupt the normal production of blood cells, but they remain in the marrow instead of entering the bloodstream, where they would be visible in a blood test. For an aleukemic patient, the white blood cell counts in the bloodstream can be normal or low. Aleukemia can occur in any of the four major types of leukemia, and is particularly common in hairy cell leukemia.
Risk Factors for Leukemia
- Use of tobacco is associated with a small increase in the risk of developing acute myeloid leukemia in adults
- Some people have a genetic predisposition towards developing leukemia
- People with chromosomal abnormalities or certain other genetic conditions have a greater risk of leukemia. For example, people with Down syndrome have a significantly increased risk of developing forms of acute leukemia (especially acute myeloid leukemia), and Fanconi anemia is a risk factor for developing acute myeloid leukemia.
- Exposure to significant ELF magnetic fields might result in twofold excess risk for leukemia for children exposed to these high levels of magnetic fields
- Race is a risk factor. Hispanics, especially those under the age of 20, are at the highest risk for leukemia, while whites, Native Americans, Asians, and Alaska Natives are at higher risk than blacks.
- Sex is also a risk factor. More men than women are diagnosed with leukemia and die from the disease. Around 30 percent more men than women have leukemia.
Diagnosis of Leukemia
Diagnosis is usually based on repeated complete blood counts and a bone marrow examination following observations of the symptoms, however, in rare cases blood tests may not show if a patient has leukemia, usually this is because the leukemia is in the early stages or has entered remission. A lymph node biopsy can be performed as well in order to diagnose certain types of leukemia in certain situations.
Following diagnosis, blood chemistry tests can be used to determine the degree of liver and kidney damage or the effects of chemotherapy on the patient. When concerns arise about visible damage due to leukemia, doctors may use an X-ray, MRI, or ultrasound. These can potentially view leukemia’s effects on such body parts as bones (X-ray), the brain (MRI), or the kidneys, spleen, and liver (ultrasound). Finally, CT scans are rarely used to check lymph nodes in the chest.
Despite the use of these methods to diagnose whether or not a patient has leukemia, many people have not been diagnosed because many of the symptoms are vague, unspecific, and can refer to other diseases.
Mutation in SPRED1 gene has been associated with a predisposition to childhood leukemia. SPRED1 gene mutations can be diagnosed with genetic sequencing.
Prevention from Leukemia
There is no way to prevent Leukemia but some risk factors can be decreased. For example; avoiding exposure to significant ELF magnetic fields and stop smoking may decrease your risk factors for Leukemia.
Treatment of Leukemia
Most forms of leukemia are treated with pharmaceutical medication, typically combined into a multi-drug chemotherapy regimen. Some are also treated with radiation therapy. In some cases, a bone marrow transplant is useful.
Acute lymphoblastic
Management of ALL focuses on control of bone marrow and systemic (whole-body) disease. Additionally, treatment must prevent leukemic cells from spreading to other sites, particularly the central nervous system (CNS) e.g. monthly lumbar punctures. In general, ALL treatment is divided into several phases:
- Induction chemotherapy to bring about bone marrow remission. For adults, standard induction plans include prednisone, vincristine, and an anthracycline drug; other drug plans may include L-asparaginase or cyclophosphamide. For children with low-risk ALL, standard therapy usually consists of three drugs (prednisone, L-asparaginase, and vincristine) for the first month of treatment.
- Consolidation therapy or intensification therapy to eliminate any remaining leukemia cells. There are many different approaches to consolidation, but it is typically a high-dose, multi-drug treatment that is undertaken for a few months. Patients with low- to average-risk ALL receive therapy with antimetabolite drugs such as methotrexate and 6-mercaptopurine (6-MP). High-risk patients receive higher drug doses of these drugs, plus additional drugs.
- CNS prophylaxis (preventive therapy) to stop the cancer from spreading to the brain and nervous system in high-risk patients. Standard prophylaxis may include radiation of the head and/or drugs delivered directly into the spine.
- Maintenance treatments with chemotherapeutic drugs to prevent disease recurrence once remission has been achieved. Maintenance therapy usually involves lower drug doses, and may continue for up to three years.
- Alternatively, allogeneic bone marrow transplantation may be appropriate for high-risk or relapsed patients.
Chronic lymphocytic
CLL treatment focuses on controlling the disease and its symptoms rather than on an outright cure. CLL is treated by chemotherapy, radiation therapy, biological therapy, or bone marrow transplantation. Symptoms are sometimes treated surgically (splenectomy removal of enlarged spleen) or by radiation therapy (“de-bulking” swollen lymph nodes).
Initial CLL treatments vary depending on the exact diagnosis and the progression of the disease, and even with the preference and experience of the health care practitioner. There are dozens of agents used for CLL therapy. An initial treatment regimen that contains fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (known as FCR) has demonstrated higher overall response rates and complete response rates.
Decision to treat
Hematologists base CLL treatment on both the stage and symptoms of the individual patient. A large group of CLL patients have low-grade disease, which does not benefit from treatment. Individuals with CLL-related complications or more advanced disease often benefit from treatment. In general, the indications for treatment are:
- Falling hemoglobin or platelet count
- Progression to a later stage of disease
- Painful, disease-related overgrowth of lymph nodes or spleen
- An increase in the rate of lymphocyte production
Treatment approach
CLL is probably incurable by present treatments. The primary chemotherapeutic plan is combination chemotherapy with chlorambucil or cyclophosphamide, plus a corticosteroid such as prednisone or prednisolone. The use of a corticosteroid has the additional benefit of suppressing some related autoimmune diseases, such as immunohemolytic anemia or immune-mediated thrombocytopenia. In resistant cases, single-agent treatments with nucleoside drugs such as fludarabine, pentostatin, or cladribine may be successful. Younger patients may consider allogeneic or autologous bone marrow transplantation.
Acute myelogenous
Many different anti-cancer drugs are effective for the treatment of AML. Treatments vary somewhat according to the age of the patient and according to the specific subtype of AML. Overall, the strategy is to control bone marrow and systemic (whole-body) disease, while offering specific treatment for the central nervous system (CNS), if involved.
In general, most oncologists rely on combinations of drugs for the initial, induction phase of chemotherapy. Such combination chemotherapy usually offers the benefits of early remission and a lower risk of disease resistance. Consolidation and maintenance treatments are intended to prevent disease recurrence. Consolidation treatment often entails a repetition of induction chemotherapy or the intensification chemotherapy with additional drugs. By contrast, maintenance treatment involves drug doses that are lower than those administered during the induction phase.
Chronic myelogenous
There are many possible treatments for CML, but the standard of care for newly diagnosed patients is imatinib (Gleevec) therapy. Compared to most anti-cancer drugs, it has relatively few side effects and can be taken orally at home. With this drug, more than 90% of patients will be able to keep the disease in check for at least five years, so that CML becomes a chronic, manageable condition.
In a more advanced, uncontrolled state, when the patient cannot tolerate imatinib, or if the patient wishes to attempt a permanent cure, then an allogeneic bone marrow transplantation may be performed. This procedure involves high-dose chemotherapy and radiation followed by infusion of bone marrow from a compatible donor. Approximately 30% of patients die from this procedure.
Hairy cell
Decision to treat:
Patients with hairy cell leukemia who are symptom-free typically do not receive immediate treatment. Treatment is generally considered necessary when the patient shows signs and symptoms such as low blood cell counts , frequent infections, unexplained bruises, anemia, or fatigue that is significant enough to disrupt the patient’s everyday life.
Typical treatment approach:
Patients who need treatment usually receive either one week of cladribine, given daily by intravenous infusion or a simple injection under the skin, or six months of pentostatin, given every four weeks by intravenous infusion. In most cases, one round of treatment will produce a prolonged remission.
Other treatments include rituximab infusion or self-injection with Interferon-alpha. In limited cases, the patient may benefit from splenectomy (removal of the spleen). These treatments are not typically given as the first treatment because their success rates are lower than cladribine or pentostatin.
T-cell prolymphocytic
Most patients with T-cell prolymphocytic leukemia, a rare and aggressive leukemia with a median survival of less than one year, require immediate treatment.
T-cell prolymphocytic leukemia is difficult to treat, and it does not respond to most available chemotherapeutic drugs. Many different treatments have been attempted, with limited success in certain patients: purine analogues (pentostatin, fludarabine, cladribine), chlorambucil, and various forms of combination chemotherapy (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, prednisone CHOP, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, prednisone [COP], vincristine, doxorubicin, prednisone, etoposide, cyclophosphamide, bleomycin VAPEC-B). Alemtuzumab (Campath), a monoclonal antibody that attacks white blood cells, has been used in treatment with greater success than previous options.
Some patients who successfully respond to treatment also undergo stem cell transplantation to consolidate the response.
Juvenile myelomonocytic
Treatment for juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia can include splenectomy, chemotherapy, and bone marrow transplantation.
